了解网页结构 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1.网页构成: 1.1 html 1.2 css 1.3 JavaScript 2.html介绍: 2.1 header部分:看到网页的元信息(比如像title标题) 2.2 body部分:可以看到网页的内容(p/a/h1等标签)
用到的网页html代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="cn"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Scraping tutorial 1 | 莫烦Python</title> <link rel="icon" href="https://morvanzhou.github.io/static/img/description/tab_icon.png"> </head> <body> <h1>爬虫测试1</h1> <p> 这是一个在 <a href="https://morvanzhou.github.io/">莫烦Python</a> <a href="https://morvanzhou.github.io/tutorials/data-manipulation/scraping/">爬虫教程</a> 中的简单测试. </p> </body> </html>
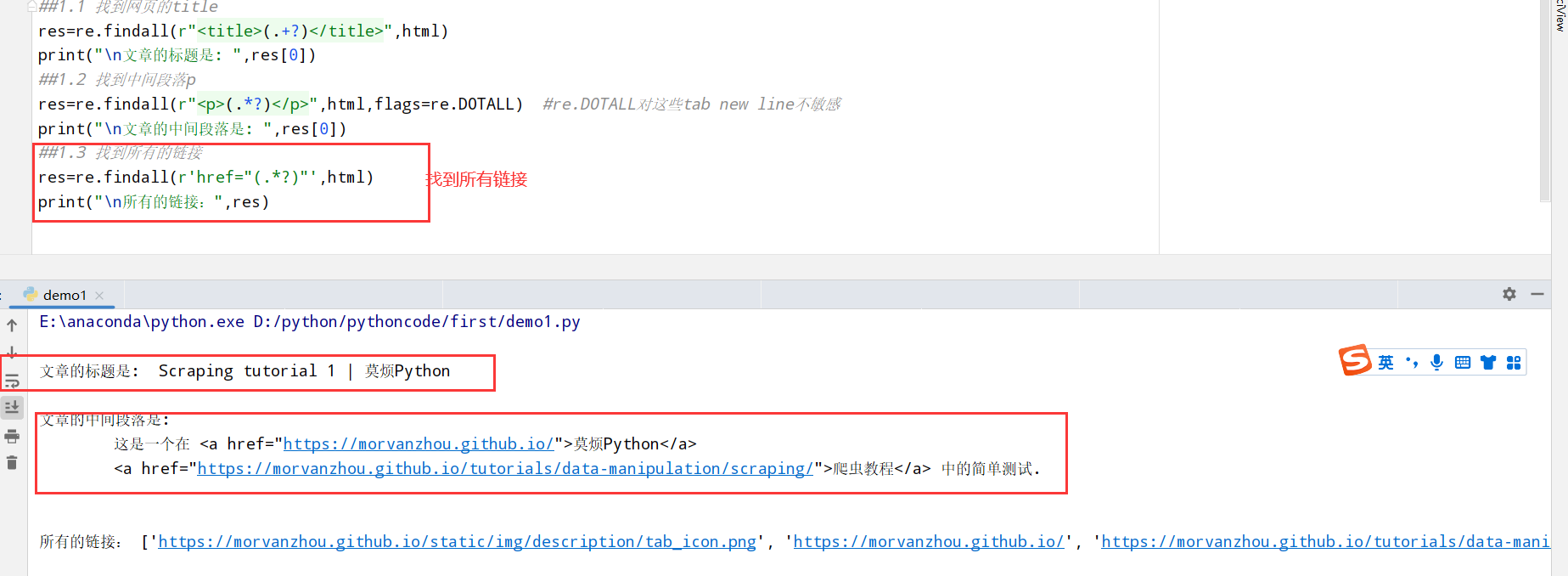
匹配网页内容(两种方式) 正则表达式(regex库) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 from urllib.request import urlopen #python自带的打开 import re #正则表达式RegEx进行文字匹配 html=urlopen("https://morvanzhou.github.io/static/scraping/basic-structure.html").read().decode('utf-8') print(html) #1.初级页面匹配用正则表达式 ##1.1 找到网页的title res=re.findall(r"<title>(.+?)</title>",html) print("\n文章的标题是: ",res[0]) ##1.2 找到中间段落p res=re.findall(r"<p>(.*?)</p>",html,flags=re.DOTALL) #re.DOTALL对这些tab new line不敏感 print("\n文章的中间段落是: ",res[0]) ##1.3 找到所有的链接 res=re.findall(r'href="(.*?)"',html) print("\n所有的链接:",res)
BeautifulSoup(bs4库的BeautifulSoup) 1 2 1.概念:是一个可以从HTML/XML文件中提取数据的Python库.它能够通过你喜欢的转换器实现惯用的文档导航,查找,修改文档的方式.Beautiful Soup会帮你节省数小时甚至数天的工作时间. 2.官网:https://www.crummy.com/software/BeautifulSoup/bs4/doc.zh/
解析网页:基础(按照标签名进行匹配) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 #和刚才正则表达式对比: from urllib.request import urlopen #python自带的打开 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup #bs4里面的 html=urlopen("https://morvanzhou.github.io/static/scraping/basic-structure.html").read().decode('utf-8') #print(html) #2.高级页面匹配用BeautifulSoup soup=BeautifulSoup(html,features='lxml') #将刚才获取的地址 --> lxml格式保存 #输出soup的h标题 print(soup.h1) #输出soup的p标签 print(soup.p) #输出soup的a标签(特别多的话可以用find_all()找到所有选项) all_href=soup.find_all('a') #将所有a找到 -- 但是里面会有很多其他杂质(<a href="xxx">爬虫教程</a>]) print(all_href) for i in all_href: print("a里面的地址:",i['href'])
解析网页:CSS(按照css的class进行匹配) 要准备的html网页:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 from urllib.request import urlopen #python自带的打开 import re #正则表达式RegEx进行文字匹配 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup #bs4里面的 html=urlopen("https://mofanpy.com/static/scraping/list.html").read().decode('utf-8') #print(html) soup=BeautifulSoup(html,features='lxml') #1.找到所有class=month的信息 month=soup.find_all('li',{"class":"month"}) #根据li标签获取class=month的信息 for m in month: print(m.get_text()) #获取li标签里面的所有文字标题 #2.找到class=jan的信息 然后在ul下面继续找ul内部的li信息(一层层嵌套) jan=soup.find('ul',{"class":'jan'}) d_jan=jan.find_all('li') for d in d_jan: print(d.get_text())
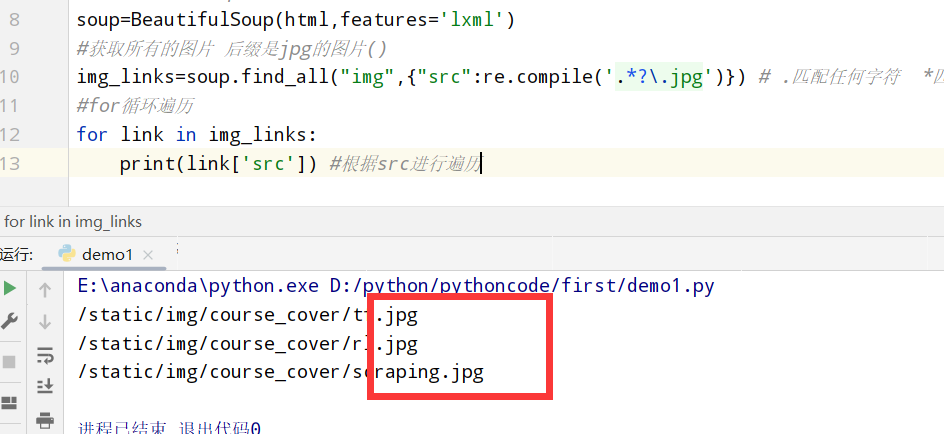
解析网页:正则表达式 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 from urllib.request import urlopen #python自带的打开 import re #正则表达式RegEx进行文字匹配 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup #bs4里面的 #获取网址 html=urlopen("https://mofanpy.com/static/scraping/table.html").read().decode('utf-8') #将页面保存到soup soup=BeautifulSoup(html,features='lxml') #获取所有的图片 后缀是jpg的图片() img_links=soup.find_all("img",{"src":re.compile('.*?\.jpg')}) # .匹配任何字符 *匹配前一个字符0/无限次 ?前面的字符可有可无 \.就是匹配. --> xxx.jpg #for循环遍历 for link in img_links: print(link['src']) #根据src进行遍历
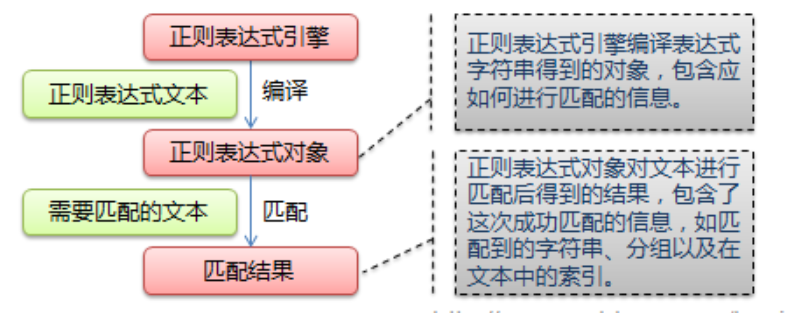
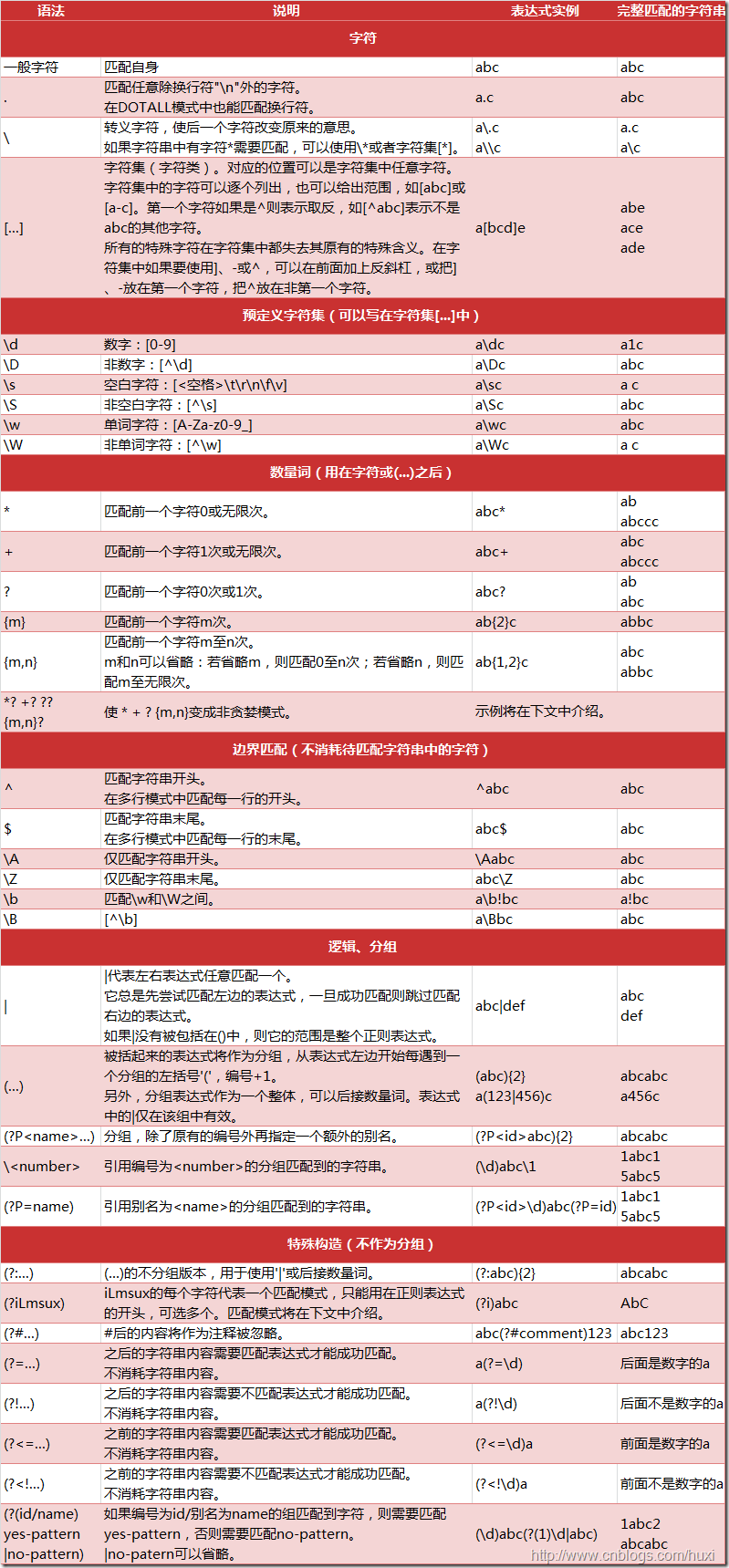
正则表达式 正则表达式匹配流程:
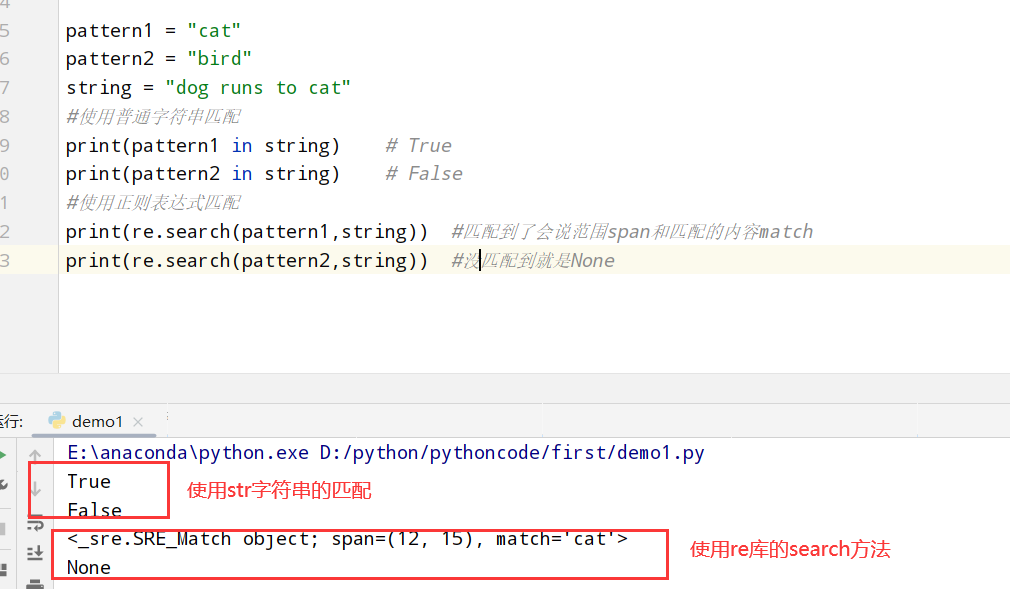
简单匹配(re.search) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 import re #正则表达式RegEx进行文字匹配 pattern1 = "cat" pattern2 = "bird" string = "dog runs to cat" #使用普通字符串匹配 print(pattern1 in string) # True print(pattern2 in string) # False #使用正则表达式匹配 print(re.search(pattern1,string)) #匹配到了会说范围span和匹配的内容match print(re.search(pattern2,string)) #没匹配到就是None
灵活匹配(pattern) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 import re #正则表达式RegEx进行文字匹配 pattern1 = "cat" pattern2 = "bird" string = "dog runs to cat" #r"xxx"表示这是正则表达式 ##1.r[au]n --> 匹配 ran/run ptn=r"r[au]n" print(re.search(ptn,string)) ##2.r[A-Z]n --> 匹配rAn/rBn.../rZn print(re.search(r"r[A-Z]n",string)) ##3.r[a-z]n --> 匹配ran/rbn.../rzn print(re.search(r"r[a-z]n",string)) ##4.r[0-9]n --> 匹配r0n/r1n.../r9n print(re.search(r"r[0-9]n]",string)) ##5.r[0-9a-z] --> 匹配可以是数字也可以是任何字母 print(re.search(r"r[0-9a-z]n",string))
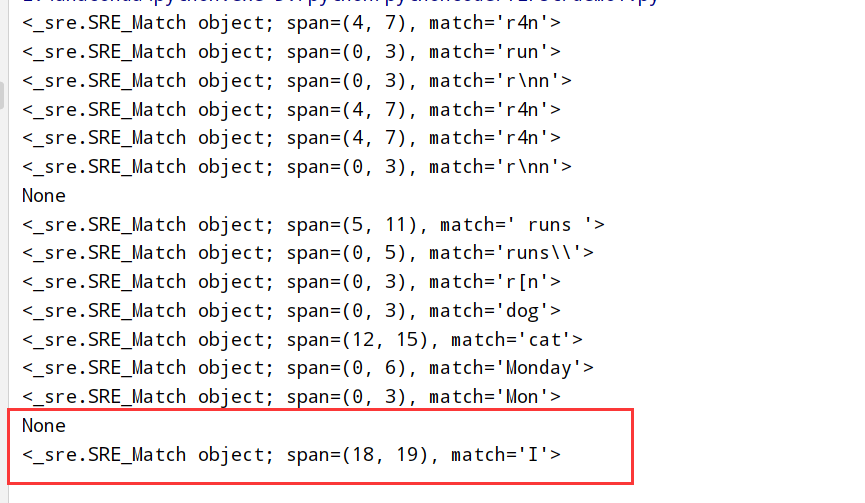
类型匹配(好多设定好的) 特殊的匹配类型:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 import re #正则表达式RegEx进行文字匹配 #匹配r(任何数字)n print(re.search(r"r\dn","run r4n")) #匹配到r4n #匹配r(不是数字)n print(re.search(r"r\Dn","run r4n")) #匹配到run #匹配r(任何white space)n --比如\t \n \r \f \v print(re.search(r"r\sn", "r\nn r4n")) #匹配到r\nn #匹配r(不是white space)n print(re.search(r"r\Sn", "r\nn r4n")) #匹配到r4n #匹配r(任何大小写字母和数字还有_ a-zA-Z0-9) print(re.search(r"r\wn", "r\nn r4n")) #匹配到r4n #匹配r(任何不是大小写字母和数字还有_ a-zA-Z0-9这个范围内) print(re.search(r"r\Wn", "r\nn r4n")) #匹配到r\nn #匹配r(只在某个字的开头/结尾的空白字符)n print(re.search(r"r\bn", "dog runs to cat")) #什么都匹配不到 #匹配(不在某个字的开头/结尾的空白字符) runs (不在某个字的开头/结尾的空白字符) print(re.search(r"\B runs \B", "dog runs to cat")) #匹配到 runs #匹配runs(\) print(re.search(r"runs\\", "runs\ to me")) #匹配到runs\\ #匹配r(任何字符 除了\n)n print(re.search(r"r.n", "r[ns to me")) #匹配r[n #匹配(开头)dog print(re.search(r"^dog", "dog runs to cat")) #匹配dog #匹配cat(结尾) print(re.search(r"cat$", "dog runs to cat")) #匹配cat #匹配Mon(day)可有可无 -->Monday和Mon都可以 print(re.search(r"Mon(day)?", "Monday")) #匹配Monday print(re.search(r"Mon(day)?", "Mon")) #匹配Mon #匹配多行字符串 #使用^形式匹配行开头的字符 string=""" dog runs to cat. I run to dog. """ #匹配不到 print(re.search(r"^I",string)) #可以匹配到 #可以对每一行单独处理 flags=re.M / flags=re.MULTILINE print(re.search(r"^I",string,flags=re.M))
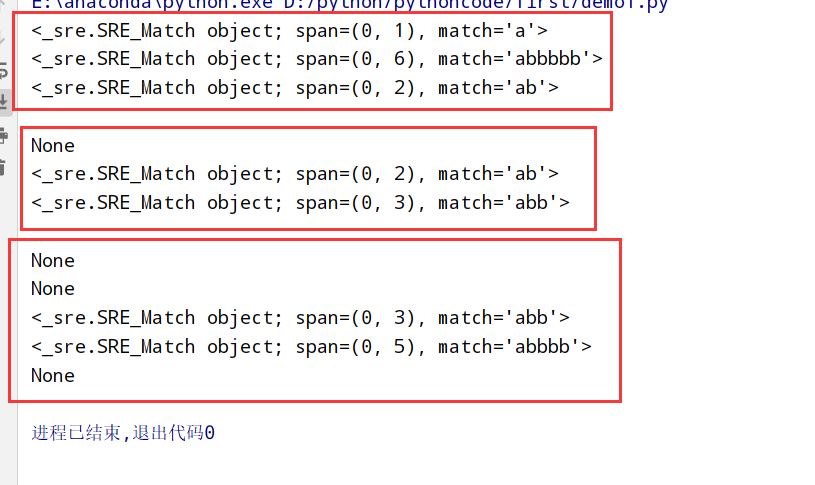
重复匹配(重复出现) 重复匹配分类:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 import re #正则表达式RegEx进行文字匹配 # *重复0次/多次 print(re.search(r"ab*","a")) # a出现一次 b出现0次/多次 a print(re.search(r"ab*","abbbbb")) # a出现一次 b出现0次/多次 abbbbb print(re.search(r"ab*","abababab")) # a出现一次 b出现0次/多次 ab print() # +重复1次/多次 print(re.search(r"ab+","a")) # a出现一次 b出现一次/多次 None print(re.search(r"ab+","ab")) #a出现一次 b出现一次/多次 ab print(re.search(r"ab+","abb")) #a出现一次 b出现一次/多次 abb print() # {n,m}重复n至m次 print(re.search(r"ab{2,10}","a")) #a出现一次 b出现2-10次 None print(re.search(r"ab{2,10}","ab")) #a出现一次 b出现2-10次 None print(re.search(r"ab{2,10}","abb")) #a出现一次 b出现2-10次 abb print(re.search(r"ab{2,10}","abbbb")) #a出现一次 b出现2-10次 abbbb print(re.search(r"ab{2,10}","ababab")) #a出现一次 b出现2-10次 None
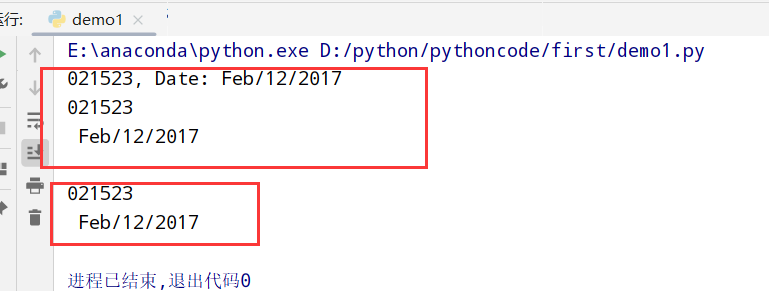
分组(re.search().group()) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 import re #正则表达式RegEx进行文字匹配 # match.group()表示返回所有组里的内容 string="ID: 021523, Date: Feb/12/2017" match=re.search(r"(\d+), Date:(.+)",string) # (\d+)表示匹配数字重复1次或者多次 (.+)表示匹配任何字符(除了\n) print(match.group()) #匹配出来 021526, Date:Feb/12/2017 print(match.group(1)) # 021526 print(match.group(2)) # Feb/12/2017 print() # ?P<名字> string= "ID: 021523, Date: Feb/12/2017" match=re.search(r"(?P<id>\d+), Date:(?P<date>.+)",string) #匹配出来 id:021526 date:Date:Feb/12/2017 print(match.group('id')) # 021523 print(match.group('date')) # Date: Feb/12/2017
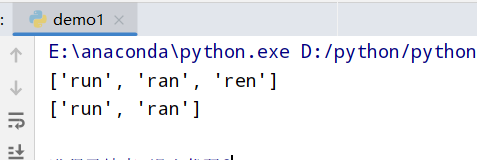
findall(全部)和or(|) 1 2 3 4 5 6 import re #正则表达式RegEx进行文字匹配 #findall是找到所有的可能 #|是找到其中一个(要么是前者要么是后者) print(re.findall(r"r[uae]n","run ran ren")) # ['run', 'ran', 'ren'] print(re.findall(r"(run|ran)","run ran ren")) # ['run', 'ran']
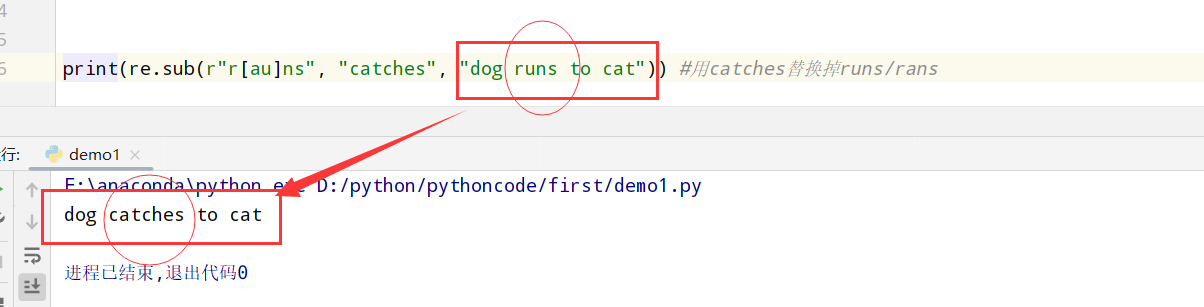
replace(re.sub()) 1 2 3 4 5 import re #正则表达式RegEx进行文字匹配 #re.sub()替换 #匹配rans|runs print(re.sub(r"r[au]ns", "catches", "dog runs to cat")) #用catches替换掉runs/rans
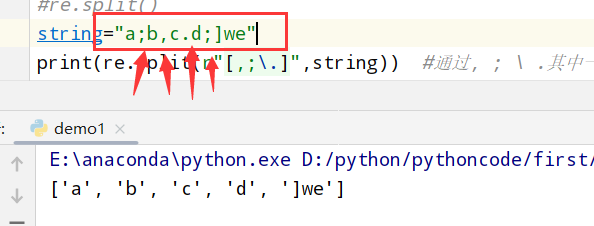
split(re.split()) 1 2 3 4 5 import re #正则表达式RegEx进行文字匹配 #re.split() string="a;b,c.d;]we" print(re.split(r"[,;\.]",string)) #通过, ; \ .其中一个进行分割成单词
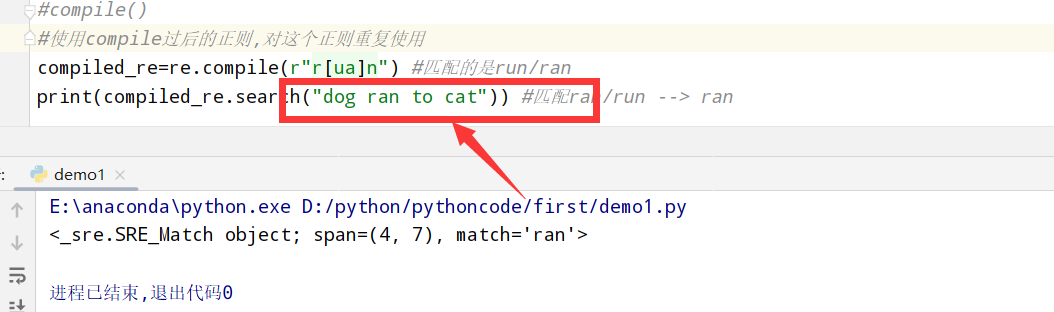
compile(将匹配的规则重复使用) 1 2 3 4 5 6 import re #正则表达式RegEx进行文字匹配 #compile() #使用compile过后的正则,对这个正则重复使用 compiled_re=re.compile(r"r[ua]n") #匹配的是run/ran print(compiled_re.search("dog ran to cat")) #匹配ran/run --> ran
小抄
小练习-爬百度百科 步骤和要求 1 2 3 4 5 6 1.设定基础url路径 2.设定his存放/item/页面 3.设置url路径 4.读取url路径 5.将html设置到soup内部 6.输出相关的标题或者其他内容
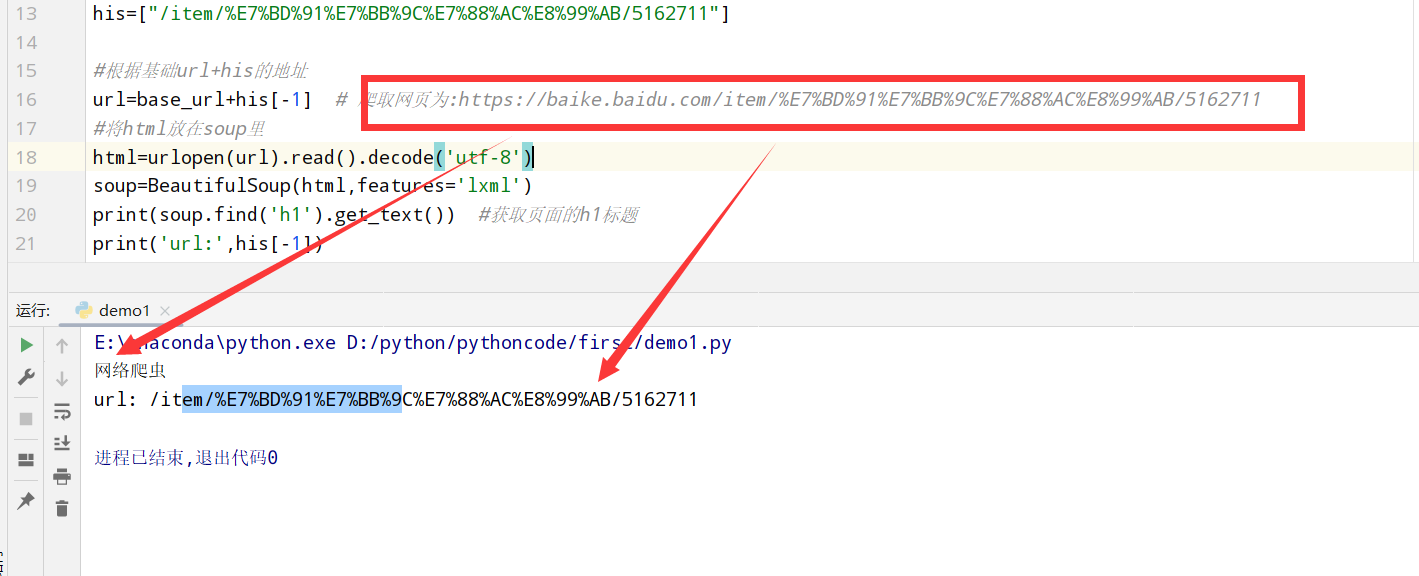
爬取一个页面 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 from urllib.request import urlopen #python自带的打开 import re #正则表达式RegEx进行文字匹配 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup #bs4里面的 import random #观看规律 #<a target="_blank" href="/item/%E8%9C%98%E8%9B%9B/8135707" data-lemmaid="8135707">蜘蛛</a> #<a target="_blank" href="/item/%E8%A0%95%E8%99%AB">蠕虫</a> #<a target="_blank" href="/item/%E9%80%9A%E7%94%A8%E6%90%9C%E7%B4%A2%E5%BC%95%E6%93%8E">通用搜索引擎</a> #基础url路径 base_url="https://baike.baidu.com" #将/item/...的页面都放在his中 his=["/item/%E7%BD%91%E7%BB%9C%E7%88%AC%E8%99%AB/5162711"] #根据基础url+his的地址 url=base_url+his[-1] # 爬取网页为:https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E7%BD%91%E7%BB%9C%E7%88%AC%E8%99%AB/5162711 #将html放在soup里 html=urlopen(url).read().decode('utf-8') soup=BeautifulSoup(html,features='lxml') print(soup.find('h1').get_text()) #获取页面的h1标题 print('url:',his[-1])
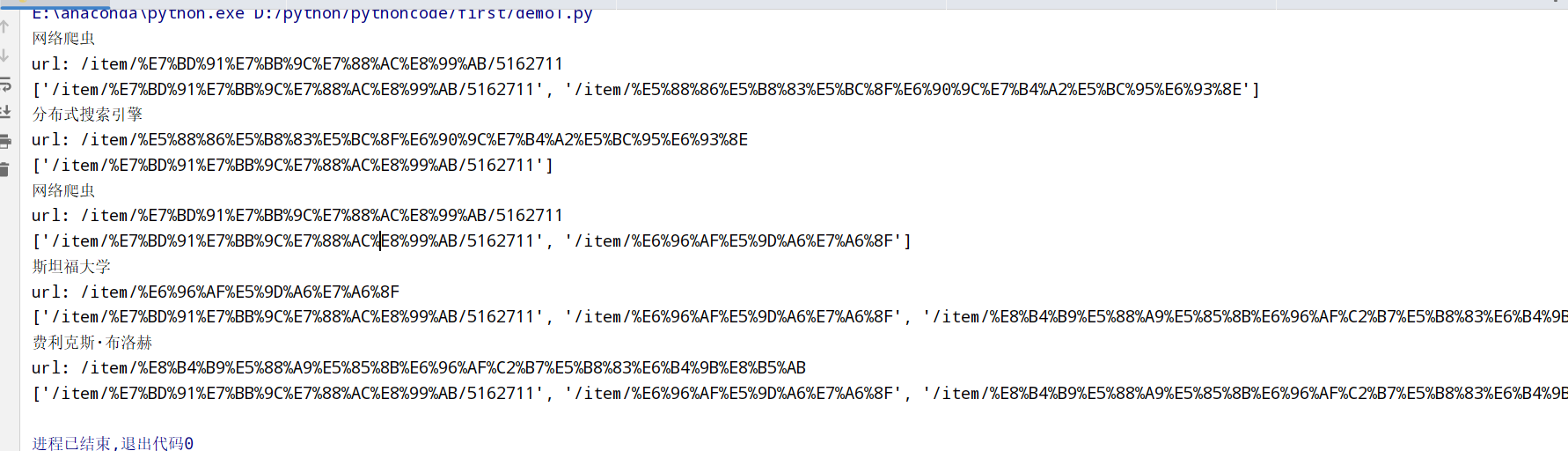
for循环爬取 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 from urllib.request import urlopen #python自带的打开 import re #正则表达式RegEx进行文字匹配 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup #bs4里面的 import random #观看规律 #<a target="_blank" href="/item/%E8%9C%98%E8%9B%9B/8135707" data-lemmaid="8135707">蜘蛛</a> #<a target="_blank" href="/item/%E8%A0%95%E8%99%AB">蠕虫</a> #<a target="_blank" href="/item/%E9%80%9A%E7%94%A8%E6%90%9C%E7%B4%A2%E5%BC%95%E6%93%8E">通用搜索引擎</a> #基础url路径 base_url="https://baike.baidu.com" #将/item/...的页面都放在his中 his=["/item/%E7%BD%91%E7%BB%9C%E7%88%AC%E8%99%AB/5162711"] for i in range(5): #根据基础url+his的地址 url=base_url+his[-1] # 爬取网页为:https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E7%BD%91%E7%BB%9C%E7%88%AC%E8%99%AB/5162711 #将html放在soup里 html=urlopen(url).read().decode('utf-8') soup=BeautifulSoup(html,features='lxml') print(soup.find('h1').get_text()) #获取页面的第一个h1标题 print('url:',his[-1]) #获取页面的标签下的地址 #找到所有url sub_urls=soup.find_all("a",{ "target":"_blank", "href":re.compile("/item/(%.{2})+$")}) #找到所有a标签 然后target="_blank" href标签都是/item/... if len(sub_urls) != 0: his.append(random.sample(sub_urls,1)[0]['href']) #如果可以就往下继续找 找到下一个标签的第一个位置 else: his.pop() #如果没有就往回走一个页面 print(his)
Requests get和post区别 1 2 1.get:取得(被动) 2.post:发送(主动)控制了服务器返回的内容,可以进行个性化服务
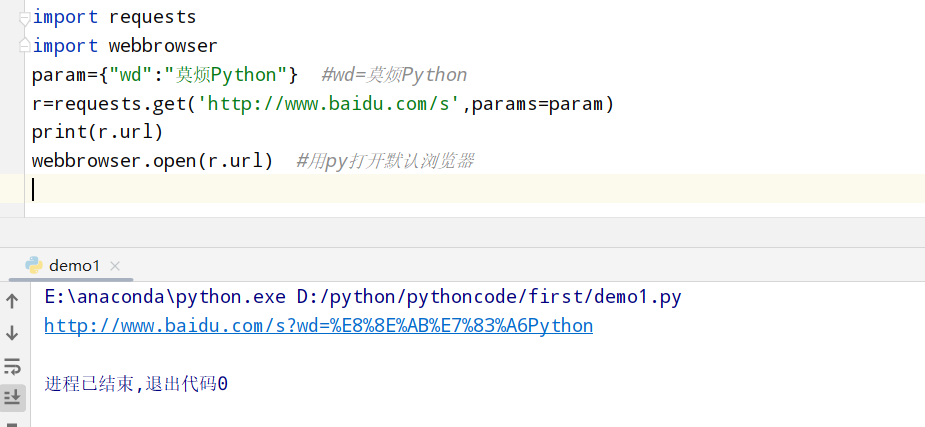
request get请求 1 2 3 4 5 6 import requests import webbrowser param={"wd":"莫烦Python"} #wd=莫烦Python r=requests.get('http://www.baidu.com/s',params=param) print(r.url) webbrowser.open(r.url) #用py打开默认浏览器
request post请求 1 2 3 4 5 import requests import webbrowser data={'firstname':'莫烦','lastname':'周'} r=requests.post('https://pythonscraping.com/pages/files/processing.php',data=data) print(r.text)
上传照片 1 2 3 4 5 import requests import webbrowser file = {'uploadFile': open('./1.jpg','rb')} r=requests.post('http://pythonscraping.com/files/processing2.php',files=file) print(r.text)
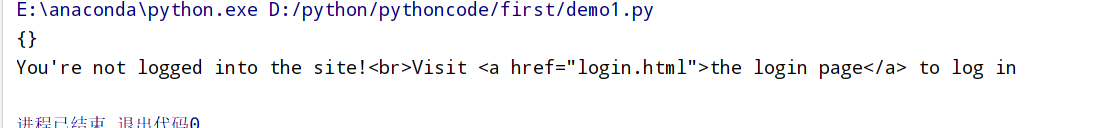
登录 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 1.使用 post 方法登录了第一个红框的 url 2.post 的时候, 使用了 Form data 中的用户名和密码 3.生成了一些cookies import requests import webbrowser from requests.packages.urllib3.exceptions import InsecureRequestWarning requests.packages.urllib3.disable_warnings(InsecureRequestWarning) payload={'username':'Lark','password':'password'} #登录的账号和密码 r=requests.post('http://pythonscraping.com/pages/cookies/welcome.php',data=payload) #将账号密码通过post上传 print(r.cookies.get_dict()) #生成cookies r=requests.get('http://pythonscraping.com/pages/cookies/profile.php',cookies=r.cookies,verify=False) #通过以前的cookies传入get请求 就可以通过已登录的名义访问get页面 print(r.text)
使用Session登录 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 import requests import webbrowser from requests.packages.urllib3.exceptions import InsecureRequestWarning requests.packages.urllib3.disable_warnings(InsecureRequestWarning) session=requests.Session() #获取session payload={'username':'Lark','password':'password'} #登录的账号和密码 r=requests.post('http://pythonscraping.com/pages/cookies/welcome.php',data=payload) #将账号密码通过post上传 print(r.cookies.get_dict()) #生成cookies r=requests.get('http://pythonscraping.com/pages/cookies/profile.php',cookies=r.cookies,verify=False) #通过以前的cookies传入get请求 就可以通过已登录的名义访问get页面 print(r.text)
下载文件(urllib.urlretrieve) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 import requests import webbrowser from requests.packages.urllib3.exceptions import InsecureRequestWarning requests.packages.urllib3.disable_warnings(InsecureRequestWarning) import os from urllib.request import urlretrieve os.makedirs('./img/',exist_ok=True) #设定一个img文件夹 IMAGE_URL="https://static.mofanpy.com/static/img/description/learning_step_flowchart.png" #图片地址 urlretrieve(IMAGE_URL,'./img/image1.png') #urllib模块提供一个下载功能urlretrieve r=requests.get(IMAGE_URL) with open('./img/image2.png', 'wb') as f: for chunk in r.iter_content(chunk_size=32): #可以通过控制每个chunk的大小 将大的文件按照一个个chunk存放 f.write(chunk)
小练习-下载美图 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 import requests import webbrowser from requests.packages.urllib3.exceptions import InsecureRequestWarning requests.packages.urllib3.disable_warnings(InsecureRequestWarning) import os from urllib.request import urlretrieve from bs4 import BeautifulSoup #获取url路径 URL="http://www.nationalgeographic.com.cn/animals/" #用soup找到带有img_list的这种ul标签 html=requests.get(URL).text soup=BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') img_ul=soup.find_all('ul', {"class": "img_list"}) #找到所有ul标签里class=img_list #从ul中找到所有的img,然后提取img的src属性(图片的网址) for ul in img_ul: imgs=ul.find_all('img') #获取所有img图片 url = img['src'] #url就是所有img图片的地址 r = requests.get(url, stream=True) image_name = url.split('/')[-1] with open('./img/%s' % image_name, 'wb') as f: for chunk in r.iter_content(chunk_size=128): f.write(chunk) print('Saved %s' % image_name)
加速爬虫(多进程分布式) 分布式爬虫(multiprocessing) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 import multiprocessing as mp import time from urllib.request import urlopen,urljoin from bs4 import BeautifulSoup import re #基本路径url base_url='https://mofanpy.com/' #爬取网页crawl def crawl(url): response = urlopen(url) time.sleep(0.1) # slightly delay for downloading return response.read().decode() #解析网页parse def parse(html): soup=BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml') urls=soup.find_all('a',{"href":re.compile('^/.+?/$')}) title=soup.find('h1').get_text().strip() page_urls = set([urljoin(base_url, url['href']) for url in urls]) # 去重 url = soup.find('meta', {'property': "og:url"})['content'] return title, page_urls, url
加速爬虫(异步加载Asyncio) Asyncio库 1 2 3 1.Python的原装库 2.Python3.5之后 3.Python3.5:async和await协同工作
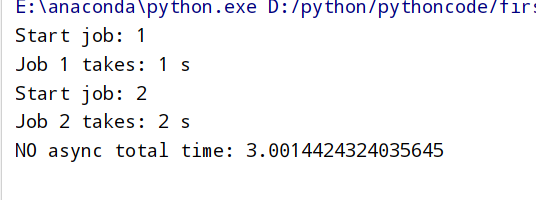
普通代码执行 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 import time #我们的job是按顺序执行的 #必须执行完job1才能开始执行job2 #而且job1需要1秒的执行时间,而job2需要2秒. 所以总时间是3秒多. def job(t): print('Start job:',t) time.sleep(t) # wait for "t" seconds print('Job',t,'takes:',t,'s') def main(): [job(t) for t in range(1, 3)] t1=time.time() main() print("NO async total time:",time.time()-t1)
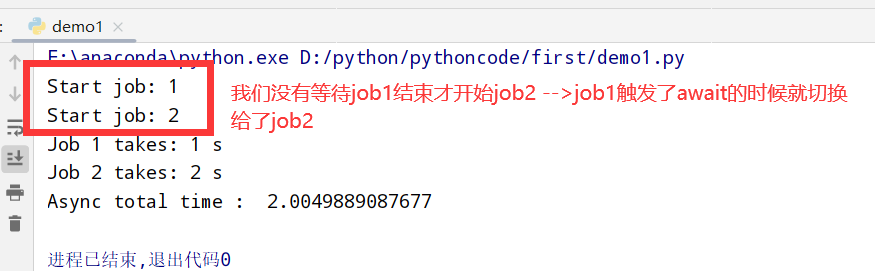
async版代码执行 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 import asyncio import time async def job(t): print('Start job:',t) await asyncio.sleep(t) # wait for "t" seconds print('Job',t,'takes:',t,'s') async def main(loop): tasks = [ loop.create_task(job(t)) for t in range(1, 3) ] # 创建任务, 但是不执行 await asyncio.wait(tasks) # 执行并等待所有任务完成 t1=time.time() loop=asyncio.get_event_loop() # 建立 loop loop.run_until_complete(main(loop)) # 执行 loop loop.close() # 关闭 loop print("Async total time:", time.time()-t1)
aiohttp aiohttp介绍:
1 2 1.aiohttp:可以将requests替换成aiohttp(换成异步requests) 2.aiohttp官网:https://docs.aiohttp.org/en/stable/index.html
一般的requests模块:
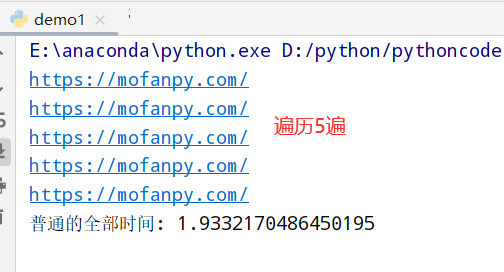
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 import time import requests #url地址 URL='https://mofanpy.com/' def normal(): for i in range(5): r=requests.get(URL) #获取url地址 url=r.url print(url) t1=time.time() normal() print("普通的全部时间:",time.time()-t1)
aiohttp模块:
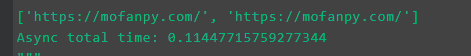
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 import time import requests import aiohttp async def job(session): response = await session.get(URL) # 等待并切换 return str(response.url) async def main(loop): async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session: # 官网推荐建立 Session 的形式 tasks = [loop.create_task(job(session)) for _ in range(2)] finished, unfinished = await asyncio.wait(tasks) all_results = [r.result() for r in finished] # 获取所有结果 print(all_results) t1 = time.time() loop=asyncio.get_event_loop() #建立loop loop.run_until_complete(main(loop)) #执行loop loop.close() #关闭loop print("Async total time:", time.time() - t1)
Selenium 概念和安装 1 2 3 4 1.概念:它能够控制你的浏览器,有模有样地学人类"看"网页 2.安装: 2.1 pip3 install selenium 2.2 分为linux和macos/windows区别
Firefox浏览器插件(Katalon Recorder) 1 2 3 1.下载:https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/katalon-automation-record/ 2.打开插件点击record进行网页操作 3.打开插件点击Export进行浏览代码
Python控制浏览器 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 from selenium import webdriver #打开火狐FireFox浏览器 #selenium.common.exceptions.WebDriverException: Message: ‘chromedriver' 就需要去根据chrome版本下载exe文件然后放在对应位置 driver=webdriver.Chrome(executable_path=r"D:\python\PyCharm 2021.1.1\plugins\python\helpers\typeshed\scripts\chromedriver.exe") #将火狐插件Export记录的代码放入 driver.get("https://mofanpy.com/") driver.find_element_by_xpath(u"//img[@alt='强化学习 (Reinforcement Learning)']").click() driver.find_element_by_link_text("About").click() driver.find_element_by_link_text(u"赞助").click() driver.find_element_by_link_text(u"数据处理 ▾").click() driver.find_element_by_link_text(u"网页爬虫").click() #得到网页html html=driver.page_source driver.get_screenshot_as_file("./img/screenshot1.png") driver.close()
Scrapy爬虫库
<
Scrapy爬虫进阶
算法汇总(Python)
>