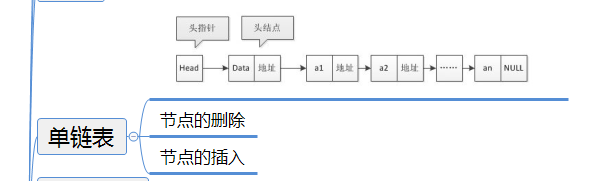
单链表
单链表图示:
单链表的基础操作
具体实现功能:
1. 添加节点(将指针不停指向下一个 判空)
2. 查询下一个节点(返回this.next)
3. 获取当前节点数据(返回this.data)
4. 判断是不是最后一个节点(只需要返回next是不是为空)
具体实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| public class Node {
//节点内容
int data;
//下一个节点
Node next;
public Node(int data){
this.data=data;
}
//追加节点
public Node append(Node node){
//当前节点
Node currentNode =this;
while(true){
//取出下一个节点赋给上一个节点
Node nextNode=currentNode.next;
if(nextNode==null)
{
break; //下一个为空就跳出
}
currentNode=nextNode; //将当前指针挪到下一个
}
//把想要追加的追加上去(上面循环已经肯定是到最后一个节点了)
currentNode.next=node;
return this; //可不停地追加 n1.append(n2).append(3)...
}
//获取下一个节点
public Node next(){
return this.next; //返回next
}
//获取数据
public int getData(){
return this.data; //获取数据
}
//判断是否是最后一个
public boolean isLast(){
return next==null;
}
}
|
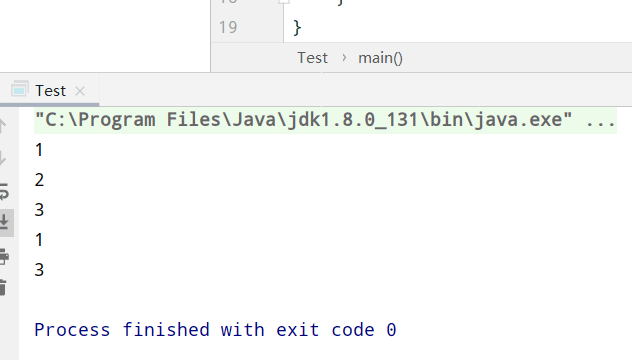
测试Test类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
//创建节点
Node n1=new Node(1);
Node n2=new Node(2);
Node n3=new Node(3);
n1.append(n2).append(n3).append(new Node(4)); // 1 --> 2 --> 3 --> 4
System.out.println(n1.next().next().next().getData()); //数据是4的节点
System.out.println(n1.next().next().next().isLast()); //判断数据是4的节点是不是最后一个
}
}
|
测试结果:
单链表删除节点(让下下一个节点连到本节点)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| //删除节点
public void removeNext(){
//获取下下一个节点
Node newNext= next.next;
//下下一个节点直接给这个节点(直接把下一个节点删除)
this.next=newNext;
}
|
单链表插入节点(先管卸下去的节点然后再连接)
方法实现解释:
1
2
3
4
5
| 假设现在是 1 --> 2 --> 3 --> 4 我们想把5插入到2后面
具体实现:
1. 将原来的下一个节点3先存到一个变量节点
2. 将5连接到2后面 1 --> 2 --> 5 || 3 --> 4
3. 现在5已经替换了3的位置 把存3的那个变量节点连到5后面 1 --> 2 --> 5 --> 3 --> 4
|
方式实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
//插入节点(先将旧的插到新的上面 新的在插到要插的位置)
public void after(Node node){
//获取下一个节点为下下一个节点
Node nextNext=next; //现在的这个下一个节点存到一个叫nextNext的节点
//新加入的节点成为这个节点的下一个节点
this.next=node;
//插入的节点后面把存的那个节点接上去
node.next=nextNext;
}
|
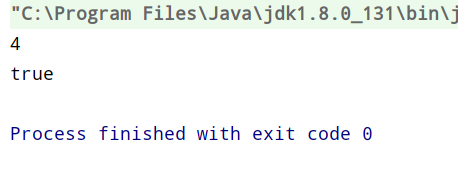
测试Test类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
//创建节点
Node n1=new Node(1);
Node n2=new Node(2);
Node n3=new Node(3);
n1.append(n2).append(n3).append(new Node(4)); // 1 --> 2 --> 3 --> 4
Node n5=new Node(5); //要插入的n5节点
n1.next().after(n5); //插入到n2的后面 n1.next()就是n2
n1.show(); //展示所有节点
}
}
|
插入n5在n2后面:
循环链表
循环链表图示:
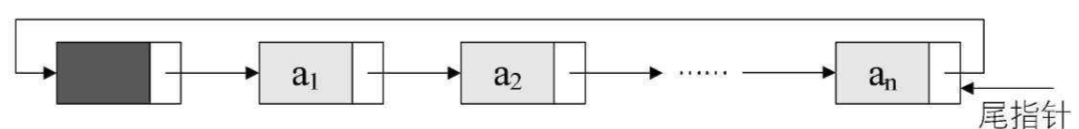
方法实现(下一个节点指向当前节点)
对比单链表: 最后一个的next要指向开头的节点
1
2
| //下一个节点
LoopNode next=this;
|
具体代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| public class LoopNode {
//节点内容
int data;
//下一个节点
LoopNode next=this;
public LoopNode(int data){
this.data=data;
}
//获取下一个节点
public LoopNode next(){
return this.next; //返回next
}
//获取数据
public int getData(){
return this.data; //获取数据
}
//判断是否是最后一个
public boolean isLast(){
return next==null;
}
//删除节点
public void removeNext(){
//获取下下一个节点
LoopNode newNext= next.next;
//下下一个节点直接给这个节点(直接把下一个节点删除)
this.next=newNext;
}
//插入节点(先将旧的插到新的上面 新的在插到要插的位置)
public void after(LoopNode node){
//获取下一个节点为下下一个节点
LoopNode nextNext=next; //下一个节点给下下一个节点
//新加入的节点成为这个节点的下一个节点
this.next=node;
//下下一个节点成为新节点的下一个节点
node.next=nextNext;
}
}
|
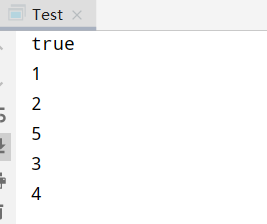
测试Test类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
//创建节点
LoopNode n1=new LoopNode(1);
LoopNode n2=new LoopNode(2);
LoopNode n3=new LoopNode(3);
LoopNode n4=new LoopNode(4);
//插入节点
n1.after(n2); //现在只有 1 --> 2
n2.after(n3); //现在是 1 --> 2 -->3
System.out.println(n1.next().getData()); // 1的下一个节点的内容应该输出2
System.out.println(n2.next().getData()); // 2的下一个节点的内容应该输出3
System.out.println(n3.next().getData()); // 3的下一个节点的内容应该输出1
}
}
|
具体实现结果:
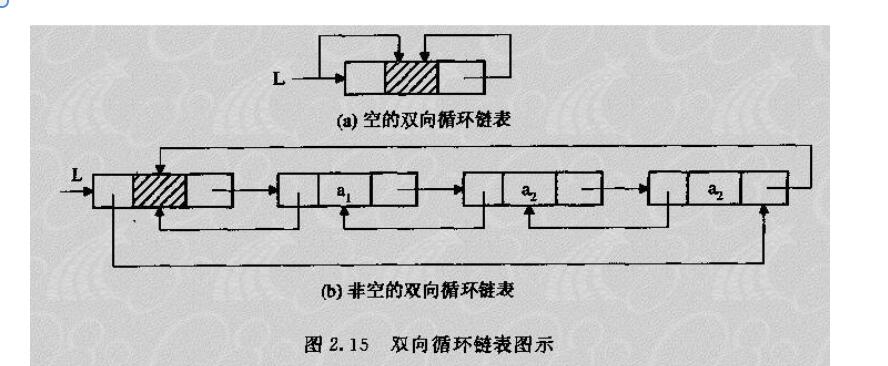
双向循环链表
双向循环链表图示:
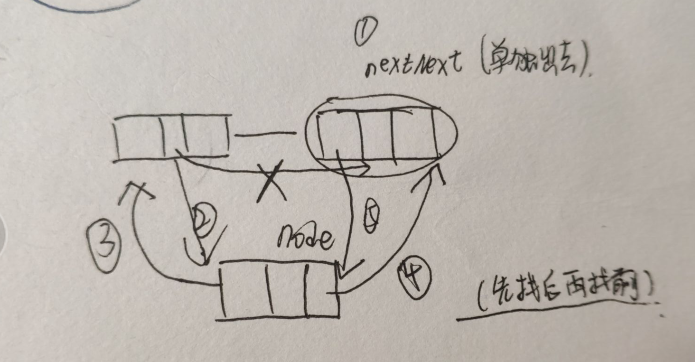
方式实现
图示解释:
具体代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| public class DoubleNode {
//上一个节点
DoubleNode pre=this; //一开始这个节点的前一个和后一个都是它自己!!!
//下一个节点
DoubleNode next=this;
//节点数据
int data;
public DoubleNode(int data) {
this.data=data;
}
//增加节点
public void after(DoubleNode node){
//原来的下一个节点
DoubleNode nextNext=next;
//把新节点作为当前节点的下一个节点
this.next=node;
//把当前节点作为新节点的前一个节点
node.pre=this;
//让原来的下一个节点作为新节点的下一个节点
node.next=nextNext;
//让原来的下一个节点的上一个节点作为新节点
nextNext.pre=node;
}
//下一个节点
public DoubleNode next() {
return this.next;
}
//上一个节点
public DoubleNode pre(){
return this.pre;
}
//获取数据
public int getData(){
return this.data;
}
}
|
测试Test类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
//创建节点
DoubleNode n1 = new DoubleNode(1);
DoubleNode n2 = new DoubleNode(2);
DoubleNode n3 = new DoubleNode(3);
//追加节点
n1.after(n2);
n2.after(n3); // 1 2 3 循环
//查看上一个,自己,下一个节点的内容
System.out.println(n2.pre().getData()); // n2的前一个节点的数据 1
System.out.println(n2.getData()); // n2的数据 2
System.out.println(n2.next().getData()); // n2的下一个节点的数据 3
System.out.println(n3.next().getData()); // n3的下一个节点的数据 1
System.out.println(n1.pre().getData()); // n1的前一个节点的数据 3
}
}
|
测试代码结果: